Mario Sato

English/Japanese/Portuguese(BR)
Graduate Student in Computer Science University of Tsukuba
Undergraduate in Business Administration INSPER - Instituto de Ensino e Pesquisa
contact: mariotsato.wb@gmail.com
View My LinkedIn Profile
My current CV
Blog:
Cardinality in CNN (ResNeXt)
The definition of cardinality is the size of the set of transformations.
In the illustration above, the architecture on the left represents ResNet, while on the right, you see ResNeXt. Both these networks utilize the split-transform-merge strategy.
This approach initially divides the input into lower dimensions through a 1x1 convolutional layer, then applies transformations using 3x3 convolutional filters, and finally integrates the outputs through a summation operation.
The key aspect of this strategy is that the transformations are derived from the same structural design, facilitating ease of implementation without necessitating specialized architectural modifications. The primary goal of ResNeXt is to effectively manage large input sizes and enhance network accuracy.
This is achieved not by adding more layers, but by increasing the cardinality - the number of parallel paths in the network. This approach effectively boosts performance while maintaining a relatively simple complexity compared to deeper networks
Source: https://www.ikomia.ai/blog/resnext-cnn-cardinality-efficiency-explained
2024/07 Inception v1 module
The first idea of the Inception model was to apply different kernel sizes to the original pixels to capture different features and learn it.
Inception v1 module optimized:
Then, they tried to reduce the computational cost by adding the 1x1 layer which enables to reduce the number of dimensions before it is used as inputs to the model. This technique can potentially reduce the convergence time.
Xception model
The Xception model came to apply a different logic that was used in Inception. It replaces these complex Inception modules with depthwise separable convolutions, which factorize a standard convolution into a depthwise convolution (applies a single filter per input channel) followed by a pointwise convolution (applies a 1x1 convolution to combine the outputs of the depthwise convolution). This reduces the number of parameters and computational cost.
2024/07 Global Average Pooling
Currently, instead of using the Dense layer in the final layer of the CNN architecture, one of the most used techniques is the Global Average Pooling. This technique consists of taking the average of the channels and reducing the number of parameters significantly.
This can be connected directly to the output layer.
model.add(GlobalAveragePooling2D())
2024/07 Vim tutorial
Play: https://vim-adventures.com/
2024/07: Resnet: pre-activation
The ResNet addressed the issue of vanishing gradient problem by introducing residual learning. Instead of learning a direct mapping from the input to the output, ResNet learns the residual, or difference, between the input and the output. This is implemented using skip connections, which allow the input to bypass one or more layers and be added directly to the output. This helps in preserving the gradient and allowing the training of much deeper networks.
Now, the ResNet with Full Pre-Activation has performed better in terms of error reduction compared to the classical ResNet. One of the biggest change the ResNet with Full Pre-Activation brought to the AI community is the reordering of the residual block. Before, the order of residual block consisted of the following order: Convolution layer, Batch Normalization, and Activation Function. This approach is often referred to as “pre-activation” because the activations are applied before the convolutions. With the implementation of the Resnet, it was set the order: Batch Normalization, Activation Function, and Convolution. This structure has been found to improve training and generalization in very deep networks.
2024/07 N-Beats
(Boris et al., 2019)
N-beats: NEURAL BASIS EXPANSION ANALYSIS FOR INTERPRETABLE TIME SERIES FORECASTING
- Key principles of the model:
- The model should be simple and generic, yet deep.
- The model should not be designed with the assumption that the input data needs to be scaled or normalized in a way that is unique to time series data. Also, the model should be robust to the scale of the input data, in other words, it shouldn’t require the model inputs to be normalized or standardized.
- The model outputs should be interpretable to the humans.
- Signal Decomposition:
- It is possible to extract useful information breaking down the model as the same way as trend and seasonality extraction approach.
- Basic block:
- The order of the hierarchy of this model consists of the following sequence: Stacks → Blocks → Basic blocks.
- The first step of this process is the assignment of the time series data to the basic block. The data is passed through a 4 layers of the FC + ReLU and after divided into two parts. Each one is passed again through another FC getting to two outputs: Backcast and Forecast. The model learns not only to output the predictions in the form of forecast but also backcast.
- Doubly residual stacking:
- The residual stacking is a technique that focuses on the difference (residuals) of the predicted values and actual values. This happens due to the fact that sometimes it is easier for the model to learn the residuals rather than the actual target values.
- Now, the double residuals stacking is a technique that doubles the stacking to make it more powerful.
- The first thing that happens is that the block predicts the difference between the best guess (backcast or forecast of the previous block) and actual values (meaning that the output is a vector that considers the aspects of the data not learned by the block 1). Then, the predictions of the residuals of the blocks are stacked together to form a new set of residuals. Next, the residual prediction is applied again, but this time, the model predicts the difference between the stacked residuals and actual values (in the Stack level). Finally, after the residual stacking, the final set of prediction is completed and it is combined to output the final predictions for the forecast.
- Parallelism:
- The model is capable of making multi-horizon forecasts in parallel.
- In other words, it can simultaneously predict multiple future time steps, which is a significant advantage for real-world forecasting tasks.
- Stacking and Loss Function:
- It describes the stacking of blocks and the choice of loss functions for training the model.
- Different block types are introduced for different types of time series forecasting problems, such as forecasting a single step ahead or multiple steps ahead.
2024/07 N-Hits
(Cristian et al., 2019)
N-HiTS: Neural Hierarchical Interpolation for Time Series Forecasting
- The N-HiTS model is a forecasting approach that extends the N-BEATS and aims to improve accuracy and computational efficiency, especially for long-horizon forecasting.
- Followings are the main topics that this research explores:
- Multi-Rate Signal Sampling:
- The multi-rate signal sampling consists of a technique to apply different kernel sizes to each block in the stack to concentrate on analyzing large scale (long periods), low-frequency content (low oscillation) to focus on long horizon forecasts.
- The first layer that the input passes through is the MaxPooling layer, with varied kernel sizes. Larger kernel sizes enables the pipeline to focus more on the long-term information than short-term.
- Also, this technique reduces the width of the input of MLP, reducing the computational cost.
- Non-Linear Regression:
- After subsampling the input signal, each block applies a non-linear regression to predict forward and backward interpolation coefficients for an MLP. These coefficients are used to synthesize the backcast and forecast outputs of the block.
- Hierarchical Interpolation:
- To address issues related to the increase in compute requirements and model expressiveness as the forecasting horizon (H) grows, N-HiTS introduces a hierarchical interpolation approach.
- The dimensionality of the interpolation coefficients is controlled by the expressiveness ratio and aims to limit the number of parameters per unit of output time. Interpolation functions (g) are used to predict all H points in the horizon, allowing for more efficient predictions.
- Neural Basis Approximation:
- N-HiTS leverages a neural basis expansion to approximate the forecast mapping. It uses multi-resolution functions (Vw) to represent the forecast functions, allowing the model to approximate infinite/dense horizons.
- The projection of these functions varies smoothly based on the input signal, and the model learns a finite number of multi-resolution coefficients to make accurate forecasts.
2023/10: Talking about @dataclass and @property.
@dataclass: By using the @dataclass, you do not need to declare the init() function in your class, because it does automatically by its own. It can facilitate you to declare the class.
@abstractmethod: Once you declare the @abstractmethod to a class, and you inherit the this class to use it to create another class, you will need to declare the function with this method in a mandatory way.
@property: It makes usage of getter and setters much easier in Object-Oriented Programming.
2023/09: Why do you need a buffer in your time series data.
Time series data buffer consists of the initial part and the final part of the source data that will be used to train a model.
Example:
|------|------------------------------|------|
t0 t1 (features and labels) t2 t3
The period of t0-t1 is the initial part, and the period of t2-t3 is the final part. Buffer is necessary to be considered when the model utilizes the features and labels that is calculated using the past and future information. For example, you can use a 180 minutes return as one of the features. However, in the very first rows of this features, the values will be NaN because you do not have a previous 180 min data. The buffer offers that information to make the model be able to use this information. Also, the same thing applies to the label. If you are using information such as return with 180 min lookahead data, then you are considering the future data. Which is only possible because you have a final part buffer in the dataset.
2023/09: CoAtNet (2021) - Overview.
- CoAtNet (Context-aware Attention Network) is a deep learning architecture, which addresses the task of object detection in images by incorporating a context-aware attention mechanism. This mechanism enables the model to focus on relevant image regions while considering contextual information, facilitating a better understanding of object relationships within their surroundings.
- Inspired by the Vision Transformer (ViT), CoAtNet adopts a patch-based architecture. It divides the input image into smaller patches and processes them individually. This patch-based approach allows the model to capture local details while maintaining a global understanding of the image, resulting in improved performance.
- CoAtNet combines the strengths of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and self-attention mechanisms in a hybrid architecture. CNNs are used for local feature extraction from image patches, while self-attention mechanisms capture global contextual dependencies. This hybrid design achieves a balance between local and global information, enhancing the model’s capabilities.
- In terms of performance, CoAtNet has shown promising results in object detection tasks. It has outperformed previous state-of-the-art models on benchmark datasets like COCO (Common Objects in Context), demonstrating improved accuracy. The model’s ability to capture contextual information and leverage attention mechanisms contributes to its superior performance.
- CoAtNet also offers various model variants, including CoAtNet-Small, etc. These variants come with different depths and computational requirements, providing flexibility in terms of model size and efficiency. Users can choose the variant that suits their specific requirements.

Source: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/coatnet-marrying-convolution-and-attention
2023/09: DenseNet (2016) - Overview.
- The DenseNet model is a convolutional network model that aims to address the vanishing gradient problem and improves the information flow between the layers in the model.
- It uses the skip connection, and dense connections by connecting the outputs of all the preceding layers to the input of subsequent layer, allowing the model to have an efficient feature reuse of information filtered by the previous layer.
- The difference between the DenseNet model with the ResNet model is that the former considers the dense connections that allows the connectivity of the previous layers with the subsequent layers, while the latter connects just the previous layer’s output with the subsequent’s input, without the connections with all other layers.
- Identity mapping is the direct propagation of the information without any alteration (F(x) + x), which is not used in the DenseNet but in ResNet.
- Residual mapping focuses on learning the difference between the input and desired output (also not used in the DenseNet).
- DenseNet optimizes parameterization by using feature concatenation instead of feature summation. This allows the network to have fewer parameters compared to traditional architectures, as the features from all preceding layers are concatenated and passed on to subsequent layers.
- Bottleneck Layer: Before the 3x3 convolution layer, the model proposes the 1x1 convolution, which reduces the number of the channels of features before the 3x3 convolution, reducing the computational complexity. In this process, the compression factor is used to determine the number of resultant feature (e.g. if 0.5, output is the half of input).

Source: https://github.com/liuzhuang13/DenseNet
2023/09: What is Data Leakage in Machine Learning (Time series data)
In this blog, I will explain about what is Data Leakage in Time series data, how it can happen and how you can avoid this to happening in your machine learning model. Data leakage happens in the moment of feature engineering. It consists of the introduction to the feature of the information that is not available in the moment of prediction. For example, let’s say that you want to predict if the price of a stock will go up or down. Then, you select one specific feature that contains the information of the date x+10. However, your label reflects the result of increase or decrease in the stock value of date x+5. Then you are using an information of the future that in the moment of prediction, it will not be available to you. In other words, in this case, you are including an information to the feature that you are trying to predict. Some of the best practices to avoid data leakage are the followings:
- Split the data to train and test subsets before any type of preprocessing steps.
-
Use the technique of Purging and Embargo to avoid mixing the training and testing dataset information. In other words, even if you separate the dataset to two parts, always include an ‘cussion’ of data that will not be used between the training and testing datasets.
continues…
Computer Science related Projects:
2023: Deploy your Object Detection app in Streamlit using YOLOv8 model (COCO dataset)
Github: HERE
DEMO in Streamlit: HERE
This is a project of object detection using YOLOv8 model with COCO dataset deployed in streamlit.

2023: Deep Learning - Cat and Dog classification with pre-trained Resnet50
Github: HERE
Cat and Dog classification using Jupyter Notebook (ipynb) with pre-trained Resnet50.

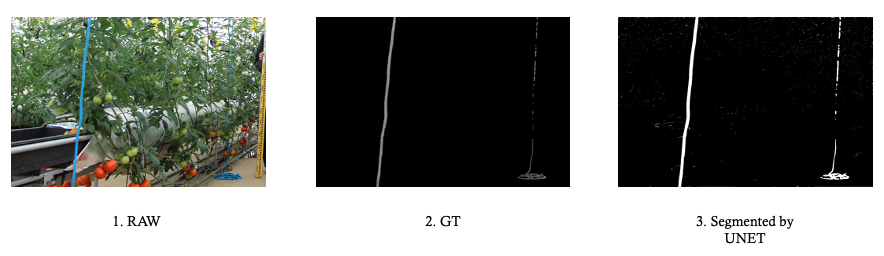
2022: Deep Learning - U-Net model applied to the rope detection
Github: HERE
A project carried on to apply the semantic segmentation to the rope detection.
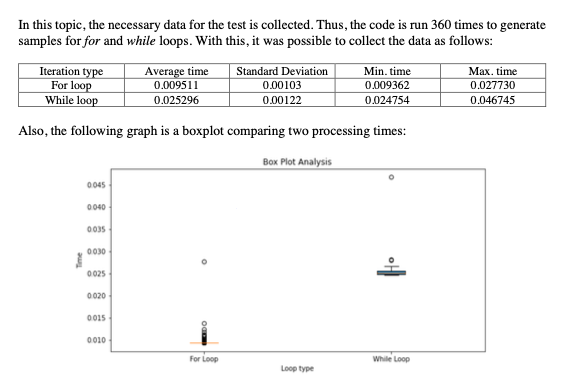
2022: For and While loop comparison
PDF: HERE
An experiment conducted with statistical analysis of comparison between For and While loop.
Conclusion: For loop is relatively faster to do the counting rather than using while loops.
Check the analysis in the pdf clicking on the image.
Experiences
- [University of Tsukuba] 2022, 2023: Research Assistant - OPERA project: LAI Index estimation using deep learning and image processing
- [University of Tsukuba] 2022, 2023: Teaching Assistant - Introduction to Information Science
- [University of Tsukuba] 2022: Teaching Assistant - Introduction to Programming using Python
Page template forked from evanca